|
|
|

|
|
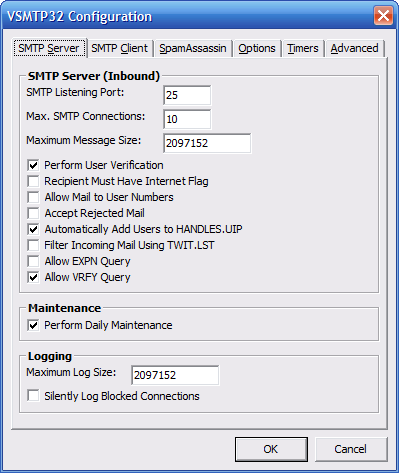
This window contains the VSMTP32 server
settings.
-
SMTP Listening Port - This
is the port number in which VSMTP32
is to listen for incoming connections.
Default = 25
-
Max. SMTP Connections - This
is the maximum number of simultaneous
SMTP connections. If this number
is exceeded, then the new connections
will be issued a control code telling
them that the server is busy.
Default = 10
-
Maximum Message Size - This value
controls what the largest message your
BBS will receive. This also includes any
file attachments that are incoming.
Default = 2097152 (2MB)
-
Perform User Verification -
If enabled, VSMTP32 will verify
that the recipient of the incoming
message is a valid account. If the
account does not exist then the
message will be rejected.
Default = On
-
Recipient Must Have Internet Flag -
If enabled then the intended user
account must have the user flag that
is specified in networks.lst. If the
account does not have the flag, then
the message is rejected.
Default = Off
-
Allow Mail to User Numbers -
If enabled then mail can be addressed
using the user's account number
in addition to their handle.
Default = Off
-
Accept Rejected Mail -
If enabled, rejected mail is allowed to be
transferred and then deleted once finished.
Default = Off
-
Automatically Add Users to HANDLES.UIP -
If enabled then if the recipient is
a valid account but the account is
not configured in the HANDLES.UIP
file, VSMTP32 will automatically
create the entry. This entry is
necessary for VADV to process the
message. This should be enabled
except for special situations.
Default = On
-
Filter Incoming Mail Using TWIT.LST -
If enabled then the incoming messages'
"From" and "Subject" headers will be
checked for words and phrases contained
in the VADV TWIT.LST file. If the
headers fail the test, the message will
be discarded. Note: If turned off,
Internet mail processed by VADV will
have it's "From" header checked using
the same file. By enabling this option,
you are stopping the message before it
gets to the BBS and doing an additional
filter on the subject line.
Default = Off
-
Allow EXPN Query - If
enabled, VSMTP32 will respect the
EXPN command and provide mailing
list information. The EXPN command
is used to retrieve the listing
of members to a mailing list.
VSMTP32 responds to this command
with the listing of users and
their email addresses. This can be
used by spammers to gain a list
of valid email addresses, so it
is usually recommended to be
disabled.
Default = Off
-
Allow VRFY Query - If
enabled, VSMTP32 will respect the
VRFY command and provide user
information. The VRFY command is
used to verify if a user account
exists. VSMTP32 responds to this
command with the user's handle
and email address. This command
is mandatory according to RFC 821.
It is possible this command could
be used by spammers to find
legitimate email addresses, so it
is usually recommended to be
disabled.
Default = On
-
Perform Daily Maintenance -
If enabled then each night at
midnight, VSMTP32 will rebuild
the HANDLES.UIP file. It is
highly recommended that you
enabled this feature and only
under certain situations should
it be disabled. It is disabled
by default to prevent the
erasure of any custom HANDLES.UIP
entries when VSMTP32 is installed.
Default = On, Recommended = On
-
Maximum Log Size - You can
control how large the VSMTP32 log
file will become before it is
reset. This value is in bytes.
Default = 2097152 (2MB)
|
|
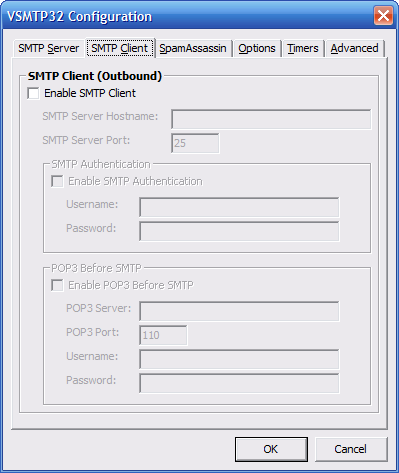
This window contains the VSMTP32 client
settings.
-
Enable SMTP Client -
If enabled, VSMTP32 will attempt
to deliver outbound email to the
configured SMTP server.
Default = Off
-
SMTP Server Hostname -
This is the hostname to your
ISP's SMTP server. VSMTP32 relays
local outbound mail to this
SMTP server for final delivery.
Default = ""
-
SMTP Server Port - If your
ISP uses a nonstandard port for
their SMTP server, you can change
it here.
Default = 25
-
Enable SMTP Authentication -
If your ISP's SMTP server requires
authentication, enable this. Enter
your username and password in the
appropriate fields. VSMTP32 tries
to detect the available methods of
authentication the server offers.
It prefers CRAM-MD5 but will
automatically switch to the more
common (and insecure) LOGIN type
if it is not available.
Default = Off
-
Enable POP3 Before SMTP -
If your ISP requires that you
perform a POP3 connection before
allowing you to send outbound
email, then enable this. Enter
your ISP's POP3 server hostname
as well as your username and
password. Each time VSMTP32
performs an outbound connection,
it will first connect to the
POP3 server so the ISP allows
the SMTP connection.
Default = Off
|
|
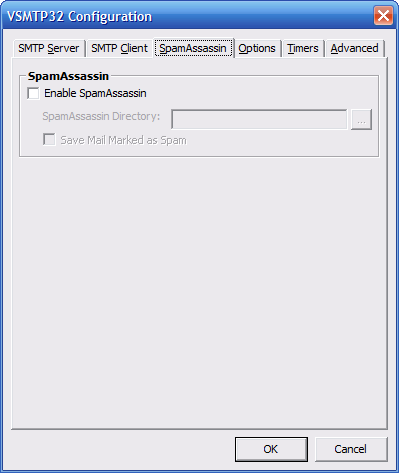
This window contains the VSMTP32 SpamAssassin
settings.
-
Enable SpamAssassin - You
can have VSMTP32 utilize SpamAssassin
to guard against SPAM. SpamAssassin
is a free application that uses
various tests to determine if a
email message is legit or not.
For information about installation and setup
with VSMTP32, visit this page.
For more information about SpamAssassin,
visit the SpamAssassin Home.
Default = Off
-
SpamAssassin Directory - Set
this field to the full path to the
directory that contains spamassassin.exe.
Default = ""
-
Save Mail Marked as Spam - If
enabled, any email that is detected
by SpamAssassin to be Spam will be
saved to the hard drive. This can
be useful for debugging the
SpamAssassin configuration or for
external processing of Spam. The
messages are saved in the
\VA\TEMP\SPAM directory. This
directory will be created automatically
by VSMTP32.
Default = Off
|
|
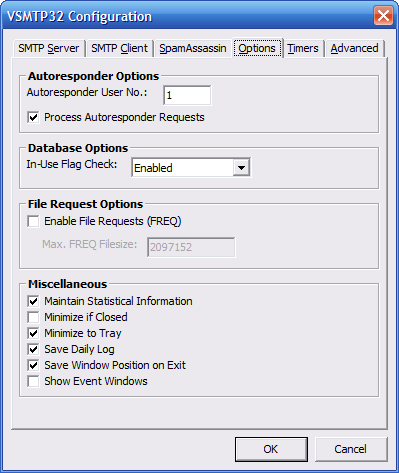
This window contains VSMTP32
options.
-
Autoresponder User No. -
You should create a special user
account on your BBS just for
autoresponder requests. If you
do not then these requests are
sent to the SysOp account and
can fill up this mailbox with
unwanted mail. Set this entry
to the user number of your
autoresponder account. If you
do not use the autoreponder or
mailing lists then it is not
necessary.
Default = 1
-
Process Autoresponder Requests -
If enabled, VSMTP32 will process any
incoming autoresponder requests. If
disabled, the BBS will handle it.
Default = On
-
In-Use Flag Check - This option checks for the
B*.FLG files used to specify that network tossing is
currently active. Options are:
-
Enabled - If the flag is found, tossing is aborted.
-
Disabled - Message tossing will execute even if the
flag exists.
-
Disabled w/ Delete - If the flag is found then it
will be deleted and message tossing will be performed.
Default = Enabled
-
Enable File Requests (FREQ) -
If enabled then anyone may email
your system at the address
SYSOP**F with the subject line
being a filename. If the filename
is found in a FREQable file area
on your BBS, then VSMTP32 will
reply to the sender with that
file as an attachment.
Default = Off
-
Max. FREQ Filesize -
This is the maximum filesize that
VSMTP32 will send outbound via a
file request. This value is in
bytes. The maximum value is 10MB.
Higher file sizes will cause
delays during processing and may
hinder the server's performance.
Default = 2097152 (2MB)
-
Maintain Statistical Information -
If enabled, VSMTP32 will save
its statistics when it closes and
remember them when reloaded.
Default = On
-
Minimize if Closed - If
enabled, VSMTP32 will minimize itself
instead of exiting if the X button
is pushed.
Default = Off
-
Minimize to System Tray -
If enabled then when VSMTP32 is
minimized it will remove itself
from the taskbar and appear in
the system tray. If disabled,
VSMTP32 will always be found
on the taskbar.
Default = On
-
Save Daily Log -
If enabled, VSMTP32 will remember
the daily log and restore it when VADV32 is loaded.
Default = On
-
Save Window Position on Exit -
If enabled then VSMTP32 will save
its current window position when
its window is closed. The next time
it is loaded, it will resume at that
position.
Default = On
-
Show Event Windows - If
enabled then any windows created
to perform a DOS task will be
visible on the taskbar. This is
generally a good idea incase the
process gets hung, but it might
also cause focus to be lost while
using other programs.
Default = Off
|
|
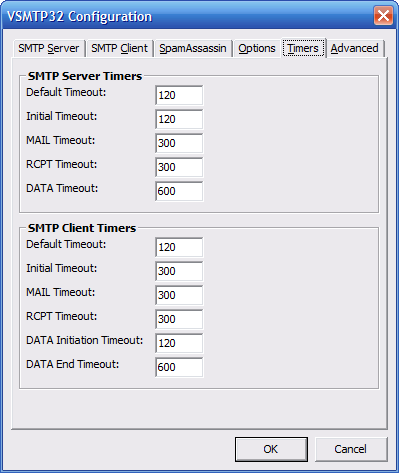
This window contains timer
settings.
-
SMTP Server Timers - These
are timeout values used by the SMTP
server.
-
SMTP Client Timers - These
are timeout values used by the SMTP
client for outgoing email.
|
|
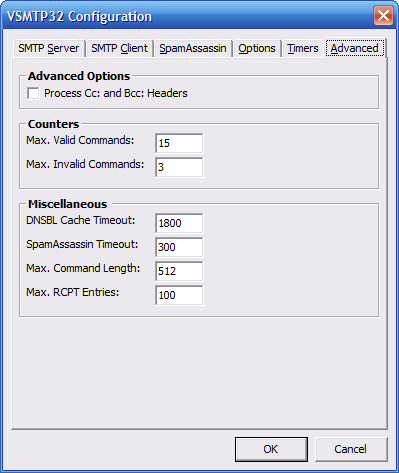
This window contains advanced
settings.
-
Process Cc: and Bcc: Headers -
This will cause VSMTP32 to literally
process all recpient headers and
attempt to send the message to
all local recipients. Only under
the most rare conditions should
this be enabled.
Default = Off
-
Max. Valid Commands - This
value represents the number of
error producing valid SMTP commands
that can be performed before the
session is terminated.
Default = 15
-
Max. Invalid Commands - This
value represents the number of
invalid/unknown commands that can
be issued before the session is
terminated.
Default = 3
-
DNSBL Cache Timeout - This is
the number of seconds that will pass
before an IP address is removed from
the DNSBL cache.
Default = 1800
-
SpamAssassin Timeout - This is
the number of seconds that VSMTP32 will
wait for a result from SpamAssassin.
Default = 300.
-
Max. Command Length - This is
the maximum number of characters that
a valid command may contain. If it
exceeds this value, then an error code
is sent back.
Default = 512
-
Max. RCPT Entries - This is the
maximum number of recipients that can
be declared in a single session.
Default = 100
|
|
If your BBS has more than one domain
name, then you can configure each name
with this option. Your main domain name
should be entered in the Internet
Configuration instead, but it doesn't
hurt if it is configured here as well.
|
|
This is the Internet Configuration
for Virtual Advanced. It is the same form
found in VADV32 and also found in VConfig.
This must be setup for VSMTP32 to work
properly. For more information, see the
VADV documentation.
|
|
Configure the autoresponder function of the BBS,
which allows automated responses to be sent to
those who email your BBS at a special address.
|
|
These forms allow you to configure
multiple mailing lists for use with
VADV. It creates the needed files used
by VADV. Note: There seems to be a problem
with VADV processing the mailing lists
through the Internet. This was
left in since it is a valid VADV feature
but is basically useless.
|
|
You can have VSMTP32 forward incoming
email to another address using this
feature. To forward to another local
user account, just enter the user account's
handle as the forwarding address. To
forward to another Internet address or to
another network address then the format
is: username@address*network number. An
example for a forwarding address is
john@mybbs.com*9 or John Doe@1:1/1*4.
|
|
This feature allows you to create a
"pseudo" account. Email sent to this
account would be accepted and passed onto
the BBS for processing - even if the
user account does not exist on the BBS or
in the HANDLES.UIP file.
|
|
You can configure aliases for user
accounts. This can be useful for having
multiple email addresses for certain
accounts.
|
|
You can filter out incoming messages
by a certain header field and its value.
This is like a much more powerful TWIT
filter. You tell it the header fields to
search for and then what values to search
in those fields. If it finds the value
in that field, then the message is blocked.
The filter is case insensitive.
|
|
You can configure the VADV TWIT filter
using this option. This filter is used
when VADV processes Internet email or
newsgroup posts. To use the TWIT filter,
enter the email address you wish to
filter out, or a word or phrase to filter
out of newsgroup subjects.
|
|
By using this feature you can specify
certain accounts that are exempt to one
or more of the filters (SpamAssassin
or Header Filter). Email that
would be typically filtered would be allowed
through to the user.
|
|
You may restrict certain countries from
connecting to your BBS. When a user connects,
VSMTP32 will determine if the caller is from
a blocked country by the connecting IP address.
|
|
If you enable the DNSBL (DNS Blackhole List)
feature, then you can specify blackhole
databases to query when an incoming
connection is created. There are various
blackhole databases available for use for
different purposes. What it does is query
the blackhole database for the IP address
of the connecting server. If the IP
address exists in the database then
the connection is refused. If the IP is
not present, then VSMTP32 allows the
server to connect and deliver email. There
are a few databases configured by default.
If caching is enabled then any IP addresses
that are rejected are cached. This speeds up
lookups and reduces the stress on the databases.
|
|
You can allow only certian IP addresses
to connect to VSMTP32, or you can exclude
certain IP addresses from connecting. This
is useful for creating a private email
system, or for keeping troublesome email
servers from connecting.
|
|
Spam traps are bogus email addresses you
specify in order to block mail servers sending
out spam. For example if you set a spam trap of
spam@example.com and your server receives a
email sent to that address, then the IP address
of the sending server will be added to the
block list. Basically you are blocking any
server that is intentionally sending mail to
non-existant user accounts.
|
|
|